Understanding Non-HDL Cholesterol: A Comprehensive Guide
Cholesterol is a term often thrown around in conversations about heart health, but it encompasses more than just the commonly known LDL and HDL types. Non-HDL cholesterol is a crucial yet often overlooked component in understanding cardiovascular risk. This article dives deep into what non-HDL cholesterol is, why it matters, and how it can impact your health. By providing a detailed exploration of this topic, we aim to surpass the current top search results in depth, clarity, and value.
Key Takeaways
- Non-HDL cholesterol includes all cholesterol types that aren’t HDL, offering a broader picture of cardiovascular risk.
- It is considered a better predictor of heart disease than LDL cholesterol alone.
- Understanding and managing non-HDL cholesterol levels can significantly impact heart health.
What is Non-HDL Cholesterol?
Non-HDL cholesterol is a term used to describe the total amount of cholesterol in your blood that is not part of high-density lipoprotein (HDL). Essentially, it includes low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and other lipid particles such as very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) and intermediate-density lipoprotein (IDL). These particles are often referred to as “bad” cholesterol because they can contribute to the buildup of plaque in arteries, leading to atherosclerosis and increasing the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
Why Focus on Non-HDL Cholesterol?
While LDL cholesterol has long been the primary focus in assessing heart disease risk, research suggests that non-HDL cholesterol may be a more reliable predictor. This is because non-HDL cholesterol encompasses all atherogenic particles, not just LDL. By considering the total amount of potentially harmful cholesterol, healthcare providers can get a more comprehensive view of an individual’s cardiovascular risk.
How is Non-HDL Cholesterol Calculated?
Calculating non-HDL cholesterol is straightforward. It is simply the total cholesterol minus the HDL cholesterol. Here’s the formula:
Total Cholesterol - HDL Cholesterol = Non-HDL Cholesterol
This calculation is advantageous because it does not require fasting, unlike the traditional LDL cholesterol test. This convenience makes it easier for individuals to monitor their cholesterol levels regularly.
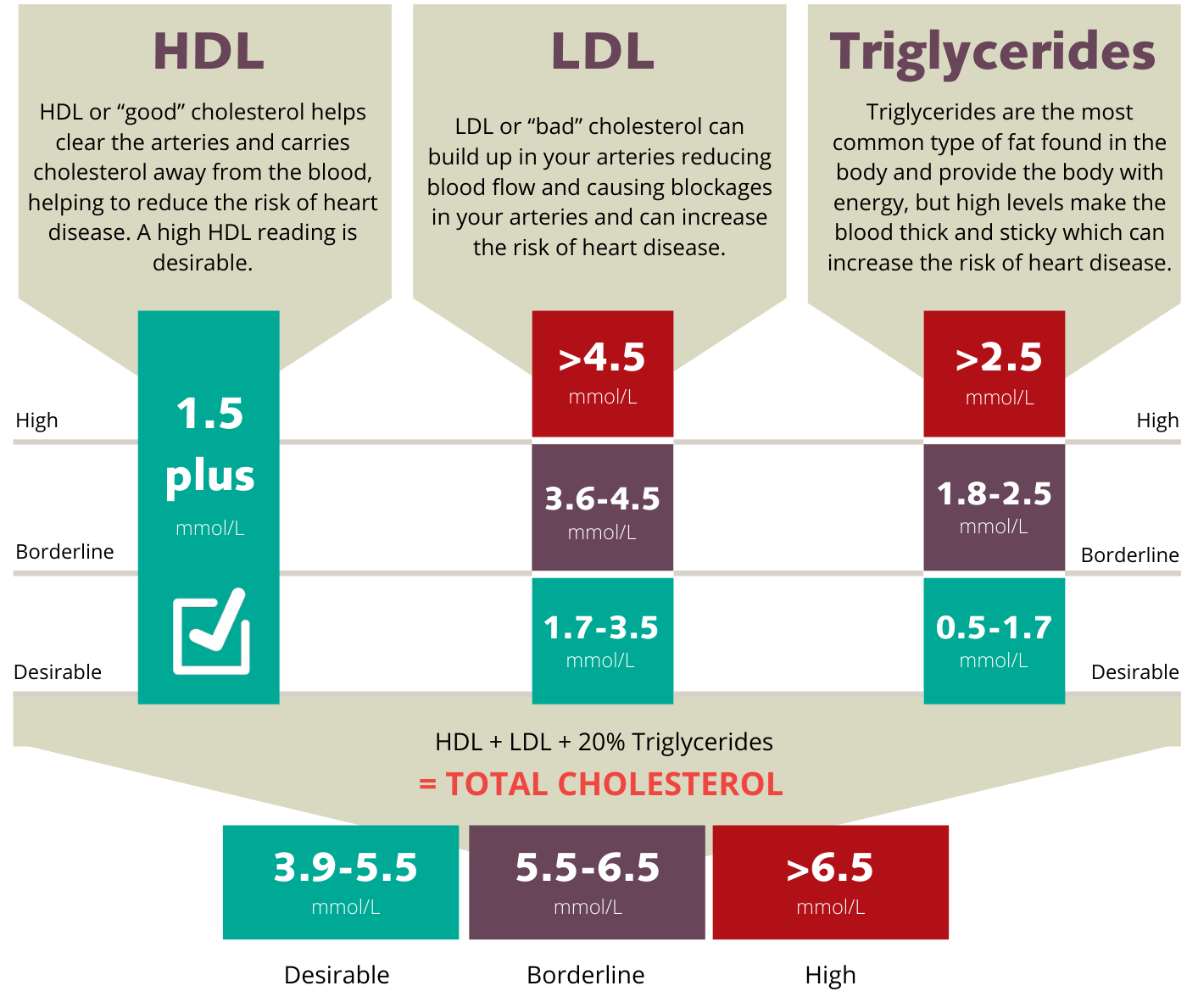
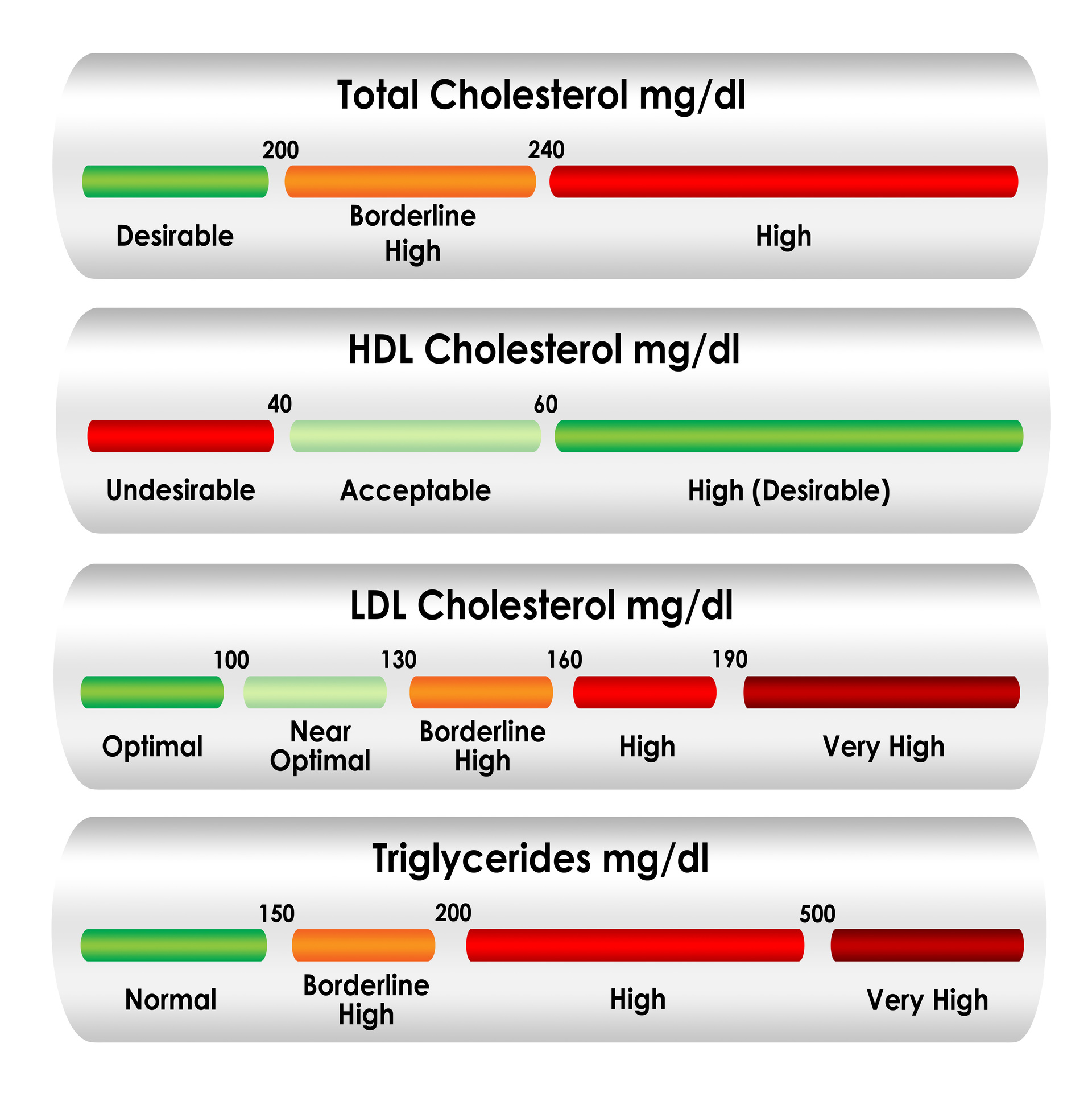
Target Levels for Non-HDL Cholesterol
Understanding target levels for non-HDL cholesterol is crucial for effective management. According to health guidelines, the optimal level for non-HDL cholesterol is generally considered to be less than 130 mg/dL. However, for individuals with existing heart disease or diabetes, the target may be lower, often less than 100 mg/dL.
Factors Affecting Non-HDL Cholesterol Levels
Several factors can influence non-HDL cholesterol levels, including:
- Diet: High intake of saturated fats and trans fats can increase non-HDL cholesterol.
- Physical Activity: Regular exercise can help lower non-HDL cholesterol levels.
- Weight: Being overweight or obese can raise non-HDL cholesterol.
- Genetics: Family history can play a significant role in cholesterol levels.
- Medical Conditions: Conditions such as diabetes and hypothyroidism can affect cholesterol levels.
Strategies to Manage Non-HDL Cholesterol
Managing non-HDL cholesterol involves a combination of lifestyle changes and, in some cases, medication. Here are some effective strategies:
1. Adopt a Heart-Healthy Diet
Focus on consuming a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Limit intake of saturated and trans fats found in processed and fried foods. Incorporate healthy fats such as those found in nuts, seeds, and fish.
2. Increase Physical Activity
Engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week. Activities like walking, cycling, and swimming can help lower cholesterol levels.
3. Maintain a Healthy Weight
Losing excess weight can significantly reduce non-HDL cholesterol levels. Aim for a gradual and sustainable weight loss through a balanced diet and regular exercise.
4. Consider Medication
In some cases, lifestyle changes alone may not be enough to achieve target cholesterol levels. Medications such as statins, niacin, and fibrates may be prescribed by healthcare providers to help manage cholesterol levels effectively.
The Role of Non-HDL Cholesterol in Heart Disease
Non-HDL cholesterol plays a significant role in the development of heart disease. High levels can lead to the accumulation of cholesterol in the arterial walls, forming plaques that narrow and harden the arteries. This condition, known as atherosclerosis, can result in reduced blood flow to the heart and other organs, increasing the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
Importance of Regular Monitoring
Regular monitoring of non-HDL cholesterol is essential for individuals at risk of cardiovascular diseases. Routine blood tests can help track cholesterol levels and assess the effectiveness of lifestyle changes or medications in managing cholesterol.
Non-HDL cholesterol is a vital component in evaluating cardiovascular risk. By understanding its significance and taking proactive steps to manage it, individuals can greatly reduce their risk of heart disease. Embracing a heart-healthy lifestyle, staying active, and working closely with healthcare providers can lead to better heart health and overall well-being.
In summary, non-HDL cholesterol offers a comprehensive view of cholesterol-related risk factors, emphasizing the importance of monitoring and managing it effectively. By following the strategies outlined in this article, you can take control of your cholesterol levels and improve your heart health.


